APIs
Application Program Interface(API), is a set of protocols that enable different software components to communicate(talk to each other) and transfer data.
APIs are everywhere—working continuously in the background to power the digital experiences that are essential to our modern lives.
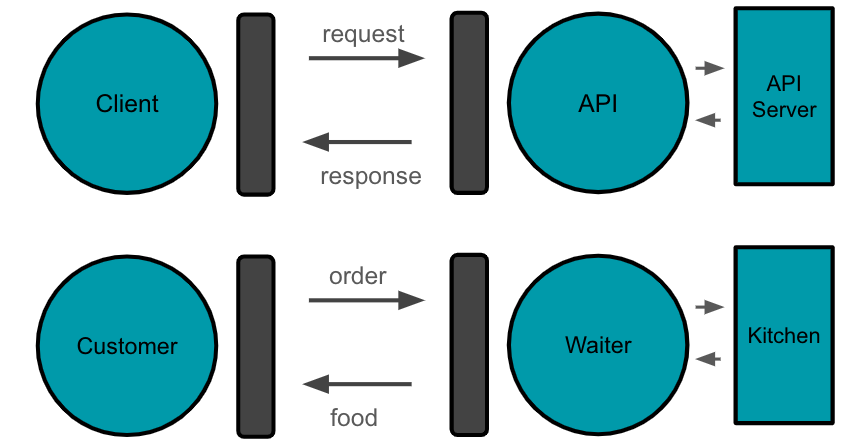
How does APIs work? APIs work similarly to ordering food at a restaurant. The customer (client) places an order (request) with the waiter (API), specifying what they want. The waiter then communicates this order to the kitchen (server), where the food is prepared. Once ready, the waiter brings the food back to the customer. Importantly, the customer doesn’t need to know or worry about how the food was made in the kitchen; they simply receive the final product. Likewise, with APIs, the client sends a request to the API, which then processes the request and interacts with the server to obtain the desired data or perform the required action. The client receives the response from the API without needing to understand the inner workings of the server or the processes involved in fulfilling the request.
REST APIs
There are some differnet API architectural styles. REST is the most popular API architecture for transferring data over the internet. REresentational State Transfer APIs: REST APIs. In a RESTful context, resources are accessible via endpoints, and operations are performed on those resources with standard HTTP methods such as GET, POST, PUT, and DELETE.
Other requently used architectural styles are: SOAP, GraphQL, Webhooks etc.